Demystifying Car Engine Spark Plug: Key Facts Revealed
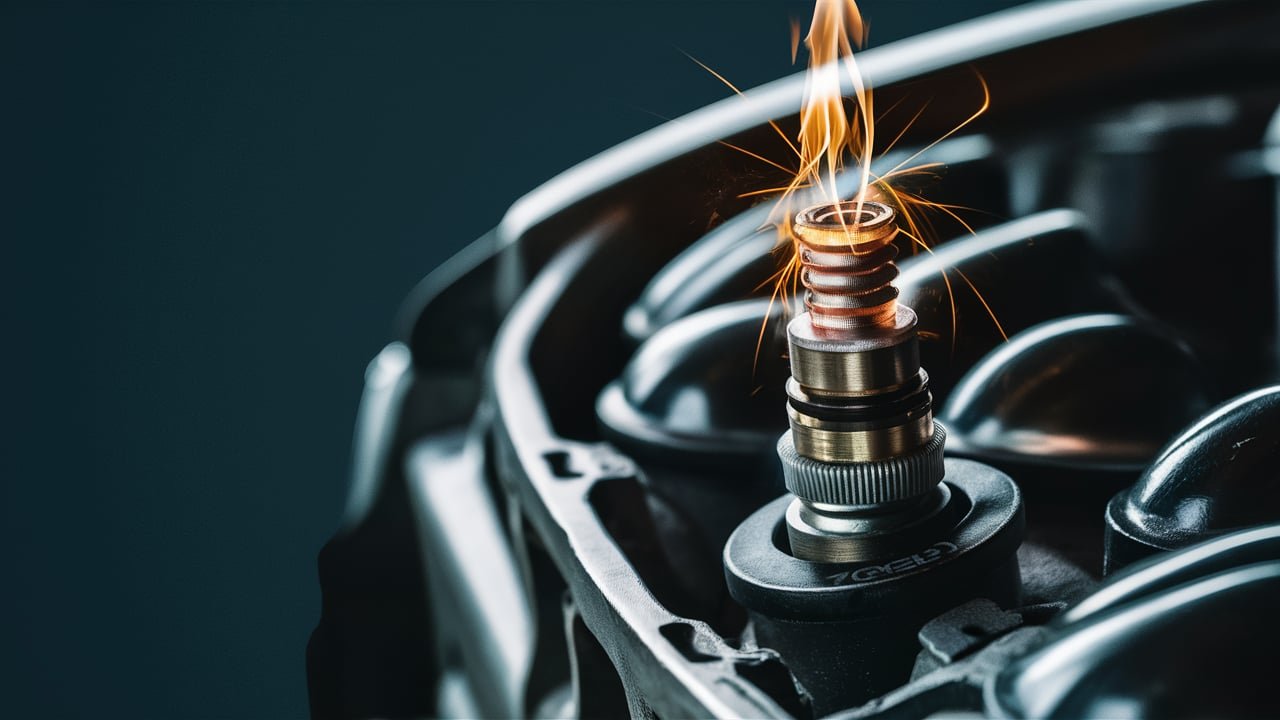
A car engine spark plug is a crucial component that plays a vital role in the functioning of an internal combustion engine. Its primary function is to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the engine’s cylinders, which is necessary for the engine to run efficiently and produce power. Here’s a detailed explanation of how spark plugs work:
- Construction: Spark plugs are constructed in three main sections: the housing, insulator, and electrodes. The housing forms the outer shell, the insulator provides electrical insulation, and the electrodes are responsible for creating the spark.
Function: When the engine is started, the ignition system delivers a high-voltage electrical signal to the spark plug. This signal creates a spark between the central electrode and the ground electrode, which is typically located at the tip of the spark plug. The spark ignites the air-fuel mixture within the cylinder, causing a small explosion that drives the piston down and ultimately powers the vehicle.
Key Features:
- High Voltage: Spark plugs operate at extremely high voltages, typically between 10,000 to 40,000 volts, to produce a hot spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture efficiently
. Insulation: The spark plug’s insulator ensures that the high voltage does not escape or short out to other components, maintaining the integrity of the electrical signal. Heat Dissipation: Spark plugs must be able to dissipate heat away from the combustion chamber to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
Signs of Bad Spark Plugs:
- Rattling or Pinging Noises: Misfires can cause unusual noises from the pistons and combustion not working correctly.
Hard Vehicle Start: Difficulty starting the engine or feeling like the engine is disjointed and jerky can indicate faulty spark plugs. Reduced Performance: Poor spark plug performance can lead to reduced engine power and efficiency.
Poor Gas Mileage: Faulty spark plugs can cause wasted fuel and decreased fuel economy.
Replacement: Spark plugs typically need to be replaced every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the type and quality of the spark plugs. Regular inspections and replacements can help maintain optimal engine performance and prevent potential damage.
In the intricate symphony of an automobile engine, one component plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the harmonious dance of power production: the spark plug. Often overlooked yet undeniably essential, spark plugs are the unsung heroes responsible for igniting the fuel-air mixture within the combustion chamber, kickstarting the fiery chain reaction that propels our vehicles forward.
As we delve into the realm of car mechanics, unraveling its complexities with precision, we unveil a world where tiny sparks wield mighty influence over engine performance.

Picture this: a vehicle’s heart beats to the rhythm of controlled explosions meticulously timed by spark plugs. These small devices serve as catalysts for combustion, transforming electrical energy into luminous sparks that ignite the volatile concoction within an engine’s cylinders.
Fundamentally simple yet technologically sophisticated, spark plugs stand as silent sentinels guarding against inefficiency and malfunction, embodying automotive engineering at its core. As we journey through this exposé on car engine spark plugs, prepare to peer beneath the hood and uncover the intricacies that drive vehicular vitality.
Understanding Car Engine Spark Plugs.
A spark plug is a small but vital component in an internal combustion engine that plays a significant role in the ignition process of the air-fuel mixture within each cylinder. By generating an electrical spark, the spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, initiating combustion to power the engine. This tiny device acts as a crucial catalyst for the entire propulsion system of a vehicle, highlighting its importance in overall engine performance.
There are several types of spark plugs available, each with distinct characteristics tailored for specific applications. Copper spark plugs, known for their affordability and good thermal conductivity, are commonly used in older vehicles.
Platinum plugs offer better longevity due to their durable properties that resist electrode erosion over time. In contrast, iridium spark plugs are praised for their exceptional durability and superior performance even in high-temperature conditions, making them popular among modern engines seeking optimal efficiency.
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of spark plugs are imperative to ensure smooth engine operation and fuel efficiency. Over time, spark plugs can deteriorate due to wear and tear from repeated use or contaminant buildup from oil or fuel additives.
Regularly checking and replacing worn-out spark plugs at recommended intervals can prevent issues like misfiring or reduced mileage, ultimately prolonging the life of the engine and maintaining peak performance levels.
By understanding the differences between various types of spark plugs and adhering to maintenance schedules, car owners can optimize their engine’s functionality and avoid costly repairs down the road.
Key Specifications to Consider.
When selecting the right spark plugs for your vehicle, it’s crucial to take into account specific key specifications that can significantly impact engine performance. One important factor to consider is the heat range of the spark plug. Heat range refers to the spark plug’s ability to dissipate heat from its firing end into the cylinder and then into the cooling system.
Choosing a spark plug with the correct heat range ensures optimal combustion efficiency. For example, in high-performance engines that generate more heat, a colder heat range spark plug may be required to prevent pre-ignition or detonation.
Another essential specification is the gap size of the spark plug, which determines the distance between the center electrode and the ground electrode. The proper gap size is crucial as it affects the initial ionization kernel formation during ignition.

A larger gap provides a stronger, more reliable spark, but if too wide, it can lead to misfires. Conversely, a smaller gap enhances longevity but might compromise performance. Finding the balance between these factors contributes to efficient combustion and engine operation.
The thread reach of a spark plug is another critical specification to consider when replacing them. This measurement indicates how far the threads extend along the body of the plug. Using a spark plug with an incorrect thread reach can result in improper seating or inadequate contact, affecting combustion efficiency and potentially causing damage to the engine over time.
Ensuring that you have precisely matched thread reach for your engine type is fundamental in maintaining optimal engine performance and reliability.
Understanding how these key specifications – heat range, gap size, and thread reach – influence your engine’s operation can guide you in making informed decisions when choosing spark plugs for your vehicle.
By paying attention to these details and selecting spark plugs that align with your engine’s requirements, you can enhance ignition efficiency, fuel economy, and overall driving experience while avoiding potential issues related to poor spark plug selection.
Replacing Spark Plugs: Step-by-Step Guide.
When tackling the task of replacing spark plugs in your vehicle, it is essential to adhere to a methodical process to ensure optimal performance. Here is a comprehensive step-by-step guide outlining the procedure:
**Step 1: Preparation – Gather Essential Tools:** Before initiating the replacement process, gather the necessary tools and materials. These typically include a ratchet, socket set (spark plug socket), gap gauge tool, anti-seize lubricant, and dielectric grease. Ensuring you have all these items on hand will streamline the replacement process.
**Step 2: Locating and Accessing Spark Plugs:** The next step involves locating and accessing the spark plugs within the engine bay. Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, spark plugs may be positioned in different areas within the engine compartment. Refer to your car’s manual or online guides for specific instructions on locating and gaining access to the spark plugs.
**Step 3: Removal and Inspection Process:** Once you have located the spark plugs, proceed with their removal using a spark plug socket attached to a ratchet. As each spark plug is removed, take time to inspect its condition carefully.
Look out for indications of fouling or damage that could compromise engine performance. This visual inspection is crucial in identifying potential issues that need addressing beyond just replacing the spark plug itself.
By following these structured steps meticulously, you can efficiently replace your car’s spark plugs without any complications. Remember that proper maintenance extends beyond just replacement; regular inspection of spark plugs can provide valuable insights into your engine’s health and potentially prevent more significant issues down the road.
Troubleshooting Common Spark Plug Issues.
When troubleshooting spark plug issues, it’s essential to be able to identify common symptoms that indicate faulty or worn-out spark plugs. One of the most prevalent signs is engine misfiring, where the engine doesn’t run smoothly and may produce a noticeable sputtering sound.
Additionally, rough idling, characterized by vibrations or fluctuations in engine speed while the vehicle is stationary, can also point towards spark plug problems. By understanding these indicators, you can swiftly address potential issues before they escalate.
Carbon fouling and oil fouling are two specific problems that can affect spark plugs. Carbon fouling occurs when carbon deposits accumulate on the spark plug’s electrodes due to incomplete combustion.

This build-up can prevent the plug from generating a strong spark, leading to performance issues. On the other hand, oil fouling happens when oil enters the combustion chamber and coats the spark plug electrodes, hindering their ability to ignite the air-fuel mixture effectively. Identifying whether your spark plugs suffer from carbon fouling or oil fouling is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action.
To tackle common spark plug problems effectively, solutions must align with the specific issue at hand. In cases of carbon fouling, cleaning or replacing the spark plugs may be necessary to restore optimal performance. Regular maintenance practices like cleaning carbons off the electrodes using specialized tools can help prevent this type of fouling.
For oil fouling scenarios, addressing underlying engine issues such as worn-out piston rings or valve seals is crucial in preventing further damage to the new set of spark plugs being installed. By diagnosing and applying tailored solutions to these common problems promptly, you ensure your car’s engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Advancements in Spark Plug Technology.
As automotive technology continues to evolve, spark plug technology has also seen significant advancements. One notable transformation is the shift from traditional copper-nickel plugs to those featuring precious metal electrodes like platinum or iridium.
These materials offer improved conductivity and longevity compared to their predecessors, resulting in more efficient ignition of the air-fuel mixture within the engine cylinders. The use of these metals not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the spark plugs, reducing the frequency of replacements required.
In recent years, innovative designs incorporating multiple ground electrodes have emerged in the realm of spark plug technology. By employing several ground electrodes around a central firing electrode, these plugs facilitate more effective combustion by creating additional pathways for the spark to travel through.
This design enhancement promotes better fuel efficiency and ensures a smoother engine operation overall. An example of this innovation can be seen in some high-performance car models where multiple ground electrode spark plugs are utilized to maximize power output while maintaining optimal fuel consumption levels.
Moreover, advanced ceramic insulators have made a notable impact on modern spark plug capabilities. Ceramic materials possess excellent thermal resistance properties, allowing spark plugs equipped with ceramic insulators to withstand extreme temperatures without compromising performance.
These insulators play a crucial role in managing heat dissipation within the combustion chamber, contributing to enhanced durability and reliability of the spark plugs over extended periods of use.
For instance, racing engines operating at high RPMs benefit greatly from spark plugs with advanced ceramic insulators that can handle intense heat stress without failing, ensuring consistent ignition under demanding conditions.
How Often Should Spark Plugs Be Replaced?
Spark plugs are a crucial component in your vehicle’s engine, and they need to be replaced regularly to maintain optimal performance and prevent potential damage. The frequency of replacement depends on various factors, including the type of spark plugs, driving conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Typical Replacement Intervals
- Standard Spark Plugs: Typically need to be replaced every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
- High-Performance Spark Plugs: May need to be replaced more frequently, every 15,000 to 30,000 miles, due to their increased power output and heat generation.
- Platinum-Tipped Spark Plugs: Can last longer, typically up to 100,000 miles or more, due to their improved durability and resistance to wear.
Factors Affecting Replacement Frequency
- Driving Conditions: Frequent city driving, towing, or driving in extreme temperatures can reduce the lifespan of spark plugs.
- Vehicle Type: Some vehicles, such as high-performance or luxury cars, may require more frequent spark plug replacements due to their advanced engine technology.
- Maintenance: Regular tune-ups and proper maintenance can help extend the life of spark plugs.
What Are the Signs That Spark Plugs Need to Be Replaced?
Spark plugs play a critical role in your vehicle’s engine, and when they start to fail, it can cause a range of issues. Here are some common signs that indicate your spark plugs need to be replaced:
Engine Performance Issues.
- Poor Engine Performance: Difficulty starting the engine, rough idling, or a lack of power can be indicative of worn-out spark plugs.
- Misfires: Unusual noises, such as rattling or pinging, can occur when spark plugs misfire, causing the engine to run inefficiently.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Faulty spark plugs can lead to decreased fuel economy, resulting in higher fuel costs.
Other Signs.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning spark plug can trigger the check engine light, indicating a problem that needs to be addressed.
- Rattling or Pinging Noises: Unusual sounds from the engine can be a sign of worn-out spark plugs.
- Difficulty Starting: Difficulty starting the engine or feeling like the engine is disjointed and jerky can indicate faulty spark plugs.
How Do Different Types of Spark Plugs Compare in Performance?
Spark plugs come in various types, each designed to cater to specific needs and driving conditions. Here’s a comparison of different types of spark plugs and their performance:

Standard Spark Plugs.
- Basic Functionality: Provide a reliable spark for standard driving conditions.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than other types of spark plugs.
- Limited Durability: Typically need to be replaced more frequently.
Platinum-Tipped Spark Plugs.
- Improved Durability: Last longer due to their platinum coating, which resists wear and corrosion.
- Enhanced Performance: Provide a more consistent and powerful spark, resulting in better engine performance.
- Higher Cost: Generally more expensive than standard spark plugs.
High-Performance Spark Plugs.
- Increased Power Output: Designed for high-performance vehicles, these spark plugs provide a more powerful spark for improved engine performance.
- Advanced Materials: Often feature advanced materials and designs for improved durability and heat dissipation.
- Higher Cost: Typically more expensive than standard spark plugs.
Iridium-Tipped Spark Plugs.
- Superior Durability: Feature an iridium coating for exceptional durability and resistance to wear.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Designed to provide a more efficient spark, resulting in better fuel economy.
- Higher Cost: Generally more expensive than platinum-tipped spark plugs.
When choosing the right spark plugs for your vehicle, consider your driving conditions, vehicle type, and performance needs. Consult your vehicle’s manual or speak with a mechanic for personalized recommendations.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of car engine spark plugs is essential for automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineering students alike.
Throughout this article, we’ve delved into the definition and role of spark plugs in igniting the air-fuel mixture within an engine, explored different types of spark plugs such as copper, platinum, and iridium with their unique characteristics, and highlighted the importance of regular maintenance and inspection to ensure optimal engine performance.
It cannot be overstated that regular maintenance of spark plugs is paramount. By considering factors like heat range, gap size, and electrode design when selecting spark plugs and following a meticulous step-by-step guide for replacement, individuals can enhance the efficiency and longevity of their engines significantly.
By troubleshooting common issues promptly and staying abreast of advancements in spark plug technology like multiple ground electrodes and advanced ceramic insulators, one can stay ahead in ensuring smooth engine operation. Remember, in the realm of car engine maintenance – the unsung heroes are often found threaded into your cylinders: the humble yet crucial spark plugs.