Unveiling the Intricacies of a Car Engine Camshaft
A car engine camshaft is a mechanical component that plays a crucial role in the functioning of an internal combustion engine. It is responsible for opening and closing the inlet and exhaust valves at the right time, ensuring that the engine operates efficiently and effectively.
Structure and Function.
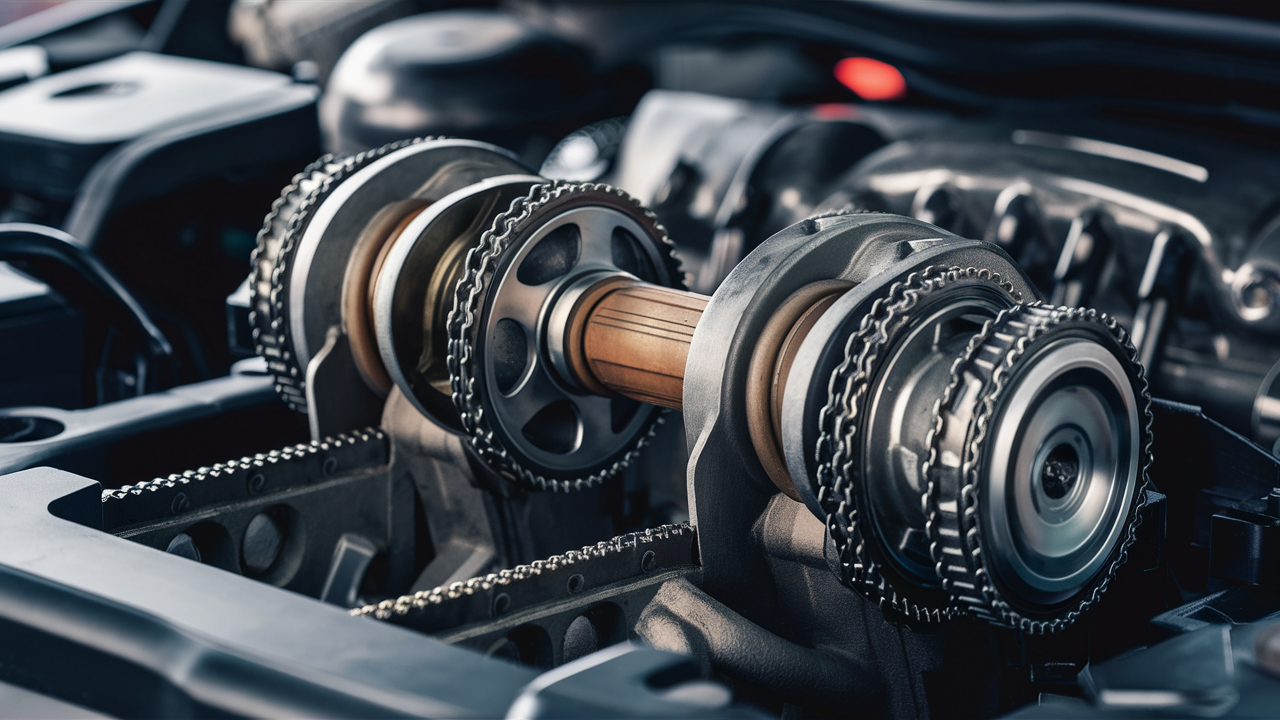
The camshaft is a metal rod located on top of the cylinders in the engine block or cylinder head. It is driven by the crankshaft through gearwheels, a toothed belt, or a timing chain. The rate of rotation of the camshaft is typically half that of the crankshaft due to a transmission ratio of 2:1.
Parts of a Camshaft.
The camshaft consists of several key components:
- Cam: This is the most important part of the camshaft, responsible for opening and closing the valves.
- Cam Follower: The part of the camshaft that is driven.
- Driveshaft: Enables movement of the camshaft structure and is linked to the crankshaft or operates independently.
- Shaft: The supporting component that binds other parts together.
- Bearings: Ensure the shaft remains upright and reduce friction during operation.
- Lobes: Provide the camshaft with the opportunity to exchange fuel-filled gases and are relative to the engine’s speed.
- Chain Sprocket: Connects to the camshaft at one end and helps maintain timing between the camshaft and crankshaft.
Types of Camshafts.
Camshafts are categorized based on the lifters used and the camshaft’s shape:
- Flat-Tappet Camshafts: Use hydraulic lifters and are relatively affordable and high-power-producing.
- Roller Camshafts: Use roller wheels and tappets for operations, providing smoother and more efficient valve operation.
Importance.
The camshaft is essential for the proper functioning of an internal combustion engine. It ensures that the valves open and close at the right times, allowing air and fuel to enter the cylinders and exhaust gases to leave. This precise timing is critical for efficient combustion and engine performance.
In summary, a car engine camshaft is a critical component that manages the opening and closing of valves in an internal combustion engine. Its structure and function are designed to ensure efficient combustion and engine performance, making it a vital part of modern engine design.
Nestled within the intricate anatomy of a car engine lies a component often overlooked by the casual observer but revered by automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineering students alike—the camshaft.
This slender yet vital shaft serves as the orchestrator of the engine, choreographing the precise movements of valves and pistons with mathematical accuracy. Understanding the nuances of this mechanical maestro unveils a world where precision meets performance, making it crucial knowledge for those who seek to decode the inner workings of an automotive masterpiece.

The camshaft, a defining element in the heart of an engine system, holds unparalleled significance for automotive aficionados thirsty for technical know-how. Mechanics rely on its rhythmic dance to diagnose and fine-tune engines with expert hands, while aspiring engineers find inspiration in its design intricacies.
As we embark on unraveling the enigmatic realm of car engine camshafts, we invite you to delve deeper into this essential cog that keeps our vehicles breathing with life—a journey that promises newfound perspectives on power delivery, efficiency optimization, and mechanical symphony harmonized by this unsung hero of automotive engineering. Join us as we ignite curiosity and illuminate the path toward unraveling every twist and turn of your car’s engine camshaft.
Understanding the Basics of a Camshaft.
A camshaft is a fundamental component within an engine that plays a crucial role in controlling the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. This mechanical shaft, typically located in the cylinder head, is synchronized with the crankshaft to ensure precise timing of these valve movements.
As the camshaft rotates, its lobes push against lifters or followers, which in turn push open the valves. This process is essential for regulating the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber while expelling exhaust gases out of it.
In various engines, different types of camshafts are utilized based on their design requirements and intended performance outcomes. For instance, overhead camshafts (OHC) have distinct advantages over traditional cam-in-block designs by reducing valvetrain mass and allowing for more precise valve control.
Moreover, performance-oriented engines may feature variable valve timing (VVT) camshafts that can alter valve timing based on engine speed and load conditions to optimize efficiency and power output.
The intricate relationship between the camshaft and other engine components such as valves and pistons highlights the interconnected nature of an internal combustion engine. The proper functioning of these elements is essential for achieving optimal engine performance.
The camshaft’s precise coordination with the movement of pistons ensures that intake and exhaust processes occur at precisely timed intervals, maximizing fuel combustion efficiency. Understanding this intricate interplay among components enables automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineering students to appreciate how each part contributes to overall engine operation seamlessly.
The functionality of a camshaft design.
The functionality of a camshaft design is crucial to the overall performance and efficiency of an engine. A detailed breakdown of the design elements reveals how various factors impact camshaft performance.
One essential aspect is the shape and size of lobes on a camshaft, which play a significant role in determining valve timing. The profile of these lobes controls when valves open and close during the engine’s operation, dictating the intake and exhaust processes that are vital for combustion efficiency.
In understanding how the shape and size of lobes influence valve timing, it becomes clear that subtle alterations can result in substantial changes in engine behavior. For instance, a camshaft with aggressive lobe profiles can lead to increased power output but may sacrifice low-end torque.
On the other hand, more conservative lobe designs prioritize fuel efficiency and smooth operation at lower RPMs. Engineers leverage this knowledge to tailor camshaft designs based on specific performance goals for different types of vehicles or engines.

Advancements in camshaft technology have continuously pushed the boundaries of engine efficiency. Modern developments focus on enhancing materials, surface treatments, and manufacturing techniques to optimize durability and performance.
For example, the integration of variable valve timing (VVT) systems allows for dynamic adjustment of camshaft positioning, improving power delivery across various engine speeds while maximizing fuel economy.
These innovations underscore how meticulous attention to camshaft design elements can revolutionize automotive engineering practices and elevate overall driving experiences for enthusiasts worldwide.
Camshaft Materials and Manufacturing Process.
When it comes to the materials used in crafting camshafts, manufacturers typically opt for strong and durable metals like cast iron, steel, or alloy steel. Each material brings its own set of properties to the table.
Cast iron, for instance, is known for its excellent wear resistance, making it a popular choice for camshafts subjected to heavy loads and high temperatures. On the other hand, steel offers superior strength without compromising on flexibility, ideal for applications where performance is a top priority.
The manufacturing process of camshafts involves intricate precision machining to ensure every detail aligns perfectly with the engine’s requirements.
Initially forged into rough shapes, these components undergo extensive machining operations such as milling, grinding, and heat treatment to achieve the desired hardness and geometry. The final finishing stages involve polishing and quality checks to guarantee optimal performance standards are met before installation.
Material selection plays a crucial role in determining the overall durability, performance efficiency, and maintenance requirements of a camshaft. For instance, utilizing alloy steel can enhance both strength and longevity compared to traditional materials like cast iron.
This choice not only improves overall engine reliability but also reduces the need for frequent replacements or repairs due to wear. Manufacturers often conduct rigorous tests to assess how different materials perform under varying conditions to ascertain which option best balances durability with operational demands.
Performance Tuning Through Camshaft Modifications.
Modifying a camshaft is a common technique used to enhance an engine’s performance by adjusting valve timing and lift. By changing how the camshaft interacts with the valves and pistons, enthusiasts can optimize power output or improve fuel efficiency.
One way this is achieved is by increasing the duration and lift of the cam lobes, allowing for more air and fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber during intake, resulting in improved horsepower and torque. For example, a performance enthusiast looking to boost their car’s acceleration may opt for a high-performance camshaft with aggressive lobe profiles.
When considering modifications to a camshaft, it’s crucial to understand the available options for optimizing different aspects of engine performance. For instance, some aftermarket camshafts are designed specifically to improve low-end torque, ideal for vehicles used for towing or off-roading activities.

On the other hand, there are camshafts focused on enhancing top-end power for racing applications where high RPM performance is essential. By selecting the right type of modification based on specific vehicle needs and usage scenarios, enthusiasts can tailor their engine’s behavior to suit their driving preferences.
Before embarking on a camshaft modification journey, it is important to consider various factors that can influence the outcome. Vehicle weight, transmission type, rear axle ratio, intended use (daily driving vs. track racing), and existing engine modifications all play a role in determining which type of camshaft modification would be most suitable.
Additionally, consulting with automotive experts or engine tuners can provide valuable insights into choosing the optimal camshaft profile that aligns with both performance goals and overall drivability requirements. By carefully evaluating these considerations upfront, enthusiasts can maximize the benefits of camshaft modifications while ensuring compatibility with their vehicle’s setup.
Troubleshooting Camshaft Issues.
Camshaft issues can manifest in various ways, indicating underlying problems within the engine’s intricate system. Common problems associated with faulty or worn-out camshafts include irregular engine idling, reduced power output, and even complete engine failure.
Automotive enthusiasts often notice a lack of smooth acceleration or unusual noises emanating from the engine bay when camshaft issues arise. Mechanics are well-versed in diagnosing these problems through thorough inspections and diagnostic tools such as stethoscopes to pinpoint irregularities in camshaft operation.
When faced with camshaft-related issues, mechanics employ specific diagnostic techniques to uncover the root cause. By conducting a visual inspection of the camshaft for visible wear or damage, checking for misalignment with other components like valves, and performing tests to measure the camshaft’s actual performance against specifications, skilled technicians can accurately diagnose the problem.
Utilizing specialized tools like borescopes to visually assess hard-to-reach areas within the engine can aid in identifying issues that may escape initial observations.
Repairing or replacing a damaged camshaft requires a methodical approach to ensure optimal engine functionality. Mechanics must first disassemble the engine carefully, removing components that obstruct access to the camshaft. Once exposed, meticulous attention is paid to detaching the old camshaft without causing further damage to surrounding parts.
Depending on the severity of the issue, repair techniques such as regrinding lobes to restore proper shape and function may be employed. However, in cases of irreparable damage, complete replacement of the camshaft is necessary, requiring precise installation procedures to guarantee proper alignment and timing within the engine’s assembly.
Conclusion: Unveiling the World Within Your Car’s Engine Camshaft.
In this exploration of the intricate realm of car engine camshafts, we have dissected the pivotal role these components play in the heart of an engine. From understanding the fundamental principles of camshaft operation to delving into the nuances of design elements affecting performance, we have unraveled essential knowledge for automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineering students alike.
The varied types of camshafts, their materials, manufacturing processes, and possibilities for performance tuning have shed light on the complexity and significance of this crucial engine component.
As we conclude our journey through the anatomy and functionality of a car engine camshaft, it is clear that a deeper comprehension of this mechanism is indispensable for anyone seeking to enhance their mastery over automotive systems.
Encouraging enthusiasts to explore further into the intricacies of camshafts empowers them with the ability to diagnose issues accurately, optimize performance efficiently, and appreciate with greater clarity the inner workings of the vehicles they admire or work on.
By continuing to unveil the mysteries within this essential component, one can truly elevate their understanding of automotive engineering to new heights.