Unveiling the Mechanism of Car Engine Brake Calipers
Delving into the intricate workings of car engine brake calipers unveils a realm where precision meets performance in the automotive world. These seemingly inconspicuous components hold a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of vehicles on the road.
As crucial elements of the braking system, brake calipers exhibit a sophisticated interplay of mechanical prowess, engineering finesse, and material science mastery.
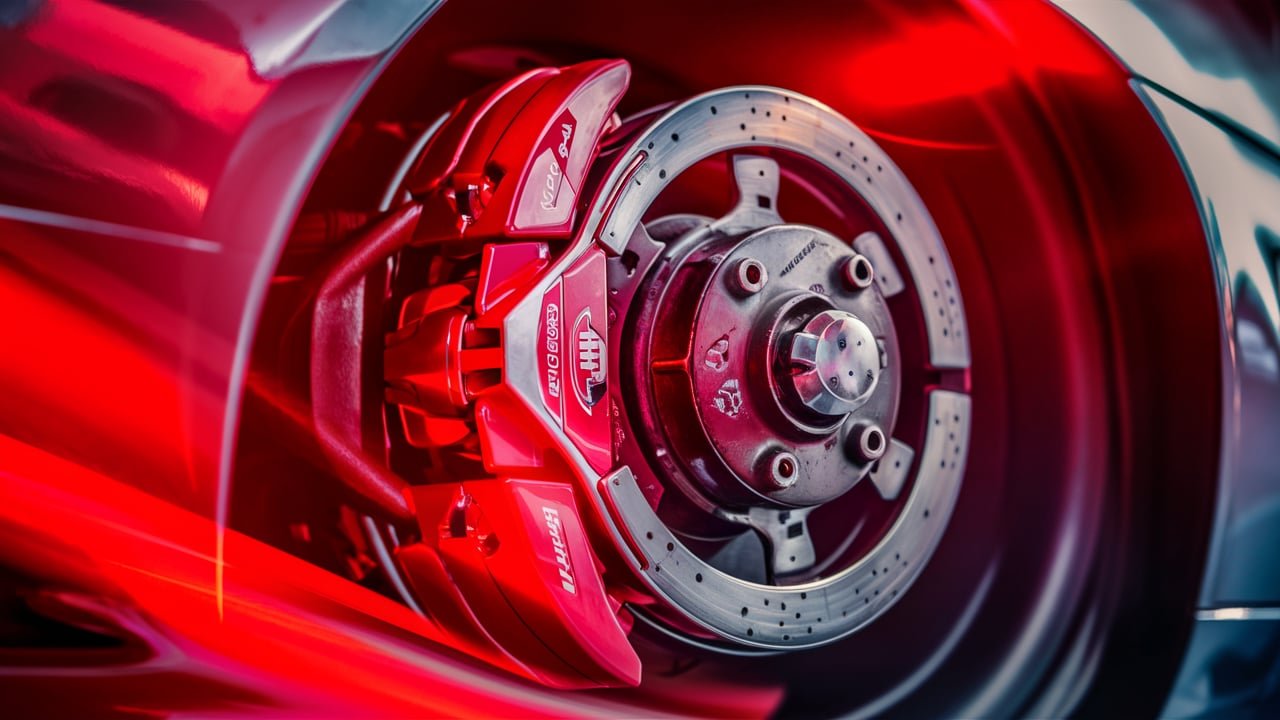
At the core of every functioning car engine brake system lie the brake calipers—a critical cog in translating mechanical force into deceleration power with exacting control. By grasping onto the rotating rotors, brake calipers harness a fundamental principle of physics to halt vehicles swiftly and safely.
Their design intricacies influence braking dynamics significantly, making them not merely static parts but dynamic performers in every braking maneuver. Understanding their anatomy—from pistons to seals—peels back layers of complexity to reveal how these unassuming entities wield immense power over vehicle deceleration.
Embark on an enlightening journey through the heart of automotive braking technology as we unravel the mechanism behind car engine brake calipers. Join us as we dissect their inner workings, explore diverse designs, address maintenance essentials, and gaze into the future of brake caliper innovations.
Let’s decipher how these unsung heroes forge paths towards safer roads and smoother rides for auto enthusiasts and mechanics alike.
Understanding Brake Calipers.
In the realm of automotive engineering, brake calipers are vital components responsible for transforming hydraulic pressure into mechanical force to halt a vehicle in motion. Essentially, a brake caliper is a device that houses the brake pads and utilizes pistons to apply pressure on the rotor, creating the friction necessary for deceleration.
When you step on the brake pedal, hydraulic fluid is sent through the brake lines to each caliper, prompting them to squeeze the brake pads against the rotating rotor surface.
Brake calipers operate via a relatively simple yet highly effective mechanism: they utilize hydraulic pressure to clamp down on the spinning rotor mounted on each wheel. This action generates friction, converting kinetic energy into heat and ultimately stopping the vehicle.
There are several types of brake calipers commonly used in automotive systems: floating calipers, fixed calipers, and sliding calipers. Floating calipers have pistons arranged on only one side of the rotor and move laterally when engaged.

Fixed calipers, conversely, have pistons on both sides that apply pressure simultaneously. Sliding calipers employ one or more pistons that slide back and forth within an assembly to exert braking force.
For instance, consider a scenario where a car approaches a red light at an intersection. As the driver applies the brakes, hydraulic pressure builds up in the system and activates the brake calipers. The floating or fixed design will then press the brake pads against the spinning rotor with precision, gradually slowing down the vehicle until it comes to a complete stop.
Understanding these different types of brake caliper mechanisms not only sheds light on how braking systems work but also underscores their importance in ensuring safe driving experiences for motorists worldwide.
Components of Brake Calipers.
Brake calipers are a crucial component in the braking system of vehicles, responsible for converting hydraulic pressure from the brake fluid into mechanical force to slow down or stop a car. A typical brake caliper assembly consists of several key parts that work together harmoniously.
These components include the caliper body, brake pads, pistons, seals, dust boots, and guide pins. The caliper body holds all the internal components in place and houses the pistons that push against the brake pads to create friction on the rotor.
In manufacturing brake calipers, materials play a significant role in determining performance and durability. Commonly used materials include aluminum, steel, or even carbon fiber composites. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties that contribute to reducing unsprung weight and improving handling.
On the other hand, steel provides strength and resistance to heat generated during braking. Manufacturers carefully select materials based on factors like vehicle weight, performance requirements, and cost considerations to optimize overall efficiency.

Pistons inside a brake caliper play a pivotal role in pressing against the brake pads when hydraulic pressure is applied. These pistons need to move smoothly within their bores to ensure even distribution of pressure on the brake pads for effective stopping power.
Seals and dust boots prevent contaminants like dirt and moisture from entering the caliper assembly, safeguarding sensitive components from damage or corrosion. Maintaining these components is essential for optimal functionality and extending the lifespan of brake calipers amidst varying road conditions and environmental elements.
Understanding how each component within a brake caliper assembly interacts underscores the precision engineering required for safe and efficient braking performance.
By recognizing the significance of materials selection in manufacturing processes along with the roles of pistons, seals, and dust boots in maintaining functionality, individuals can appreciate the intricate design behind this critical automotive system component.
An awareness of these details not only aids in routine maintenance but also sheds light on the technological advancements driving innovation in modern braking systems to enhance vehicle safety and performance standards continuously.
Types of Brake Caliper Designs.
In the realm of automotive engineering, brake calipers come in various designs tailored to meet specific performance objectives. The most common types include single-piston, dual-piston, and multi-piston configurations.
Single-piston calipers feature a piston on one side of the rotor and are typically found in smaller vehicles with less demanding braking requirements. These calipers operate efficiently but may lack the sheer stopping power needed for high-performance applications.
Dual-piston brake calipers, as the name suggests, incorporate two pistons on either side of the rotor. This design offers improved braking force distribution and more even pad wear compared to single-piston calipers. Dual-piston setups are often favored in mid-range vehicles where a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness is key.
On the other hand, multi-piston brake calipers utilize three or more pistons per caliper, providing enhanced braking power and pedal feedback ideal for sports cars or heavy-duty trucks that demand superior stopping capabilities under intense conditions.

Each brake caliper design presents distinct advantages and disadvantages concerning braking efficiency. While single-piston calipers are simpler in construction and cost-effective, they may not deliver the same level of performance as dual- or multi-piston variants.
Dual-piston calipers strike a balance between effectiveness and affordability, making them versatile for a wide range of vehicle types. In contrast, multi-piston calipers excel in high-performance scenarios by offering precise modulation and increased clamping force, albeit at a higher price point due to their intricate design.
Specific applications dictate which brake caliper design shines based on unique performance requirements. For instance, a sports car designed for track use would benefit significantly from the precision control provided by multi-piston brake calipers during aggressive braking maneuvers at high speeds.
In contrast, a city commuter vehicle might find sufficient braking performance with dual-piston calipers without the added complexity or cost associated with a multi-piston setup. Understanding these distinctions helps automotive professionals and enthusiasts alike make informed decisions when selecting brake systems tailored to their intended use cases.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting.
Routine maintenance is crucial to uphold the longevity and safety of brake calipers in automotive systems. To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to inspect brake calipers regularly for signs of wear or damage.
Routine checks should include verifying the condition of the brake pads, ensuring proper alignment, and confirming that the caliper pistons move freely without any sticking. Additionally, periodic lubrication of moving parts can help prevent rust and improve overall functionality.
Common issues encountered with brake calipers involve sticking pistons or leaks, which can impact braking efficiency and pose safety risks. When faced with sticking pistons causing uneven brake pad wear or reduced braking power, a thorough inspection and cleaning of the caliper assembly are necessary.
In cases of leaks where brake fluid seeps out from the caliper, it is essential to identify the source promptly to prevent hydraulic system failure. Addressing these issues promptly not only ensures safe operation but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire braking system.

Proper lubrication plays a pivotal role in maintaining brake calipers’ functionality and preventing premature wear. Applying high-temperature grease at contact points between moving components within the caliper assembly helps reduce friction and ensures smooth operation.
Furthermore, regular inspections allow for early detection of potential problems such as worn seals or dust boots that could compromise braking performance. By adhering to recommended maintenance practices and addressing issues proactively, car owners can optimize the reliability and safety of their vehicle’s braking system for enhanced driving experience.
Innovations in Brake Caliper Technology.
As automotive technology progresses, innovations in brake caliper technology are playing a significant role in enhancing the efficiency and performance of modern vehicles. One notable advancement is the integration of electronic calipers, which utilize sensors and actuators to improve braking precision and response times.
Electronic calipers can adjust brake force distribution more dynamically, leading to smoother stops and reduced wear on brake components. This technological leap not only enhances safety but also contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience for enthusiasts who appreciate precise control over their vehicle.
Another groundbreaking development in brake caliper technology is the adoption of carbon ceramic brakes. These brakes are known for their exceptional performance under high heat conditions, making them ideal for sports cars and high-performance vehicles.
Carbon ceramic brakes offer advantages such as reduced weight compared to traditional iron brakes, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and handling. Additionally, their durability ensures longevity and reliability even under extreme driving conditions.
As car manufacturers strive for lighter yet stronger braking solutions, carbon ceramic brakes have become a prominent feature in the automotive industry.
Looking ahead, future trends in brake caliper technology.
Looking ahead, future trends in brake caliper technology continue to focus on enhancing safety and efficiency. One emerging trend is the integration of regenerative braking systems that capture energy during deceleration and store it for later use, ultimately improving fuel economy and reducing emissions.
By harnessing kinetic energy that would otherwise be wasted as heat during braking, regenerative systems represent a sustainable approach towards optimizing vehicle performance.
Moreover, advancements in materials science may lead to the development of even lighter yet robust brake components, further pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of safety standards and environmental impact within the automotive sector.

Innovations in brake caliper technology are revolutionizing how vehicles operate by prioritizing safety, performance, and sustainability. From electronic calipers enhancing braking precision to carbon ceramic brakes redefining durability and weight reduction standards, these advancements showcase the ongoing pursuit of excellence in automotive engineering.
As future trends continue to shape brake caliper technology with a focus on efficiency and environmental consciousness through regenerative systems and advanced materials, drivers can look forward to safer roads and more eco-friendly driving experiences fueled by cutting-edge innovations in automotive braking mechanisms.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, delving into the intricate workings of car engine brake calipers has unveiled a world where precision engineering marries safety seamlessly. From understanding the fundamental mechanism of how brake calipers stop a vehicle by clamping on the rotor to exploring the various types and designs like floating, fixed, single-piston, dual-piston, and multi-piston configurations, it becomes evident that every component plays a crucial role in the braking system’s efficiency.
The detailed breakdown of brake caliper parts highlighted the significance of pistons, seals, and dust boots in maintaining optimal functionality. Furthermore, discussing materials used in manufacturing and their impact on performance shed light on the importance of quality craftsmanship.
It is imperative to underscore that regular maintenance routines coupled with effective troubleshooting techniques are essential for ensuring longevity and safety on the roads. By emphasizing proper lubrication practices and periodic inspections to detect issues early on, car enthusiasts and automotive professionals can prevent premature wear or potential malfunctions in brake calipers.
Additionally, exploring innovative technologies such as electronic calipers and regenerative braking systems showcased how advancements are continually shaping the landscape of brake caliper technology. Understanding these developments leads not only to improved performance but also contributes significantly to enhancing overall vehicle safety standards.
Ultimately, as we unveil the mechanisms behind car engine brake calipers, we recognize their pivotal role in both vehicle safety and performance – solidifying their status as indispensable components within automotive systems.