Unveiling the Intricacies of Car Engine Radiators
The intricate dance of heat dissipation within a vehicle’s engine system relies on a fundamental component—the car engine radiator. Defined as a crucial part of the cooling mechanism, the radiator serves as the unsung hero tirelessly combating thermal extremes to maintain optimal performance.
Understanding the inner workings of this mechanical marvel unveils a world where precision engineering meets environmental physics, guiding automotive enthusiasts and engineering students alike through a labyrinth of technical intricacies.
Within the symphony of mechanisms that power an automobile, the radiator emerges as a vital player in ensuring sustainability and longevity. Beyond its outward appearance lies a sophisticated network designed to facilitate efficient heat exchange and prevent overheating—a threat that looms over every mechanical operation.
Appreciating the multifaceted role played by radiators underlines the indispensable nature of these devices in maintaining peak functionality within vehicle cooling systems, thus solidifying their status as linchpins in automotive engineering evolution.
Unveiling the mosaic of components and principles governing car engine radiators illuminates not just their significance but also beckons us into a realm where temperature regulation is both science and art.
Understanding Car Engine Radiators.
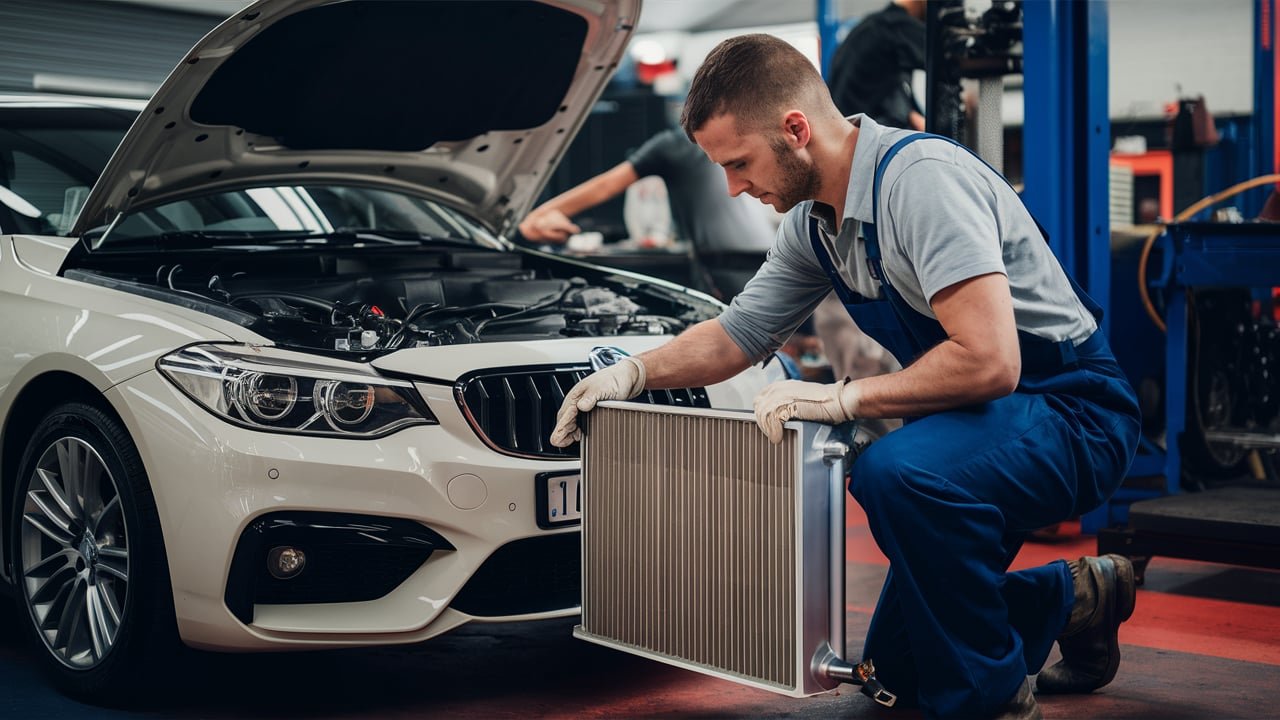
A car engine radiator, a critical component of the vehicle’s cooling system, comprises several key elements. The core, typically made of aluminum or copper, is where heat exchange occurs. Coolant tubes run through the core, allowing hot coolant from the engine to dissipate its heat as airflow passes through.
Attached to the core are tanks – one for collecting hot coolant from the engine and another for receiving cooled liquid after heat exchange. These tanks have openings for hoses that facilitate the circulation of coolant.

Radiators play a fundamental role in maintaining an optimal operating temperature within a vehicle’s engine. As the hot coolant travels from the engine to the radiator, it releases heat to the surrounding air through convection.
This process effectively cools down the liquid, which then returns to continue absorbing excess heat from the engine components, preventing overheating. By enabling this transfer of thermal energy outside the car, radiators help regulate engine temperatures within safe limits.
Coolant acts as a crucial medium in the cooling process orchestrated by radiators. Typically a mix of water and antifreeze, coolant not only helps in displacing excess heat but also prevents freezing in cold conditions and inhibits corrosion within the cooling system.
As it absorbs heat from various engine parts, becoming heated in turn, it flows into the radiator for cooling before being pumped back to dissipate more warmth. The continuous circulation of coolant ensures that engines operate at efficient temperatures while guarding against damages caused by overheating.
Common Radiator Issues and Troubleshooting.
Car engine radiators are intricate systems crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperatures, but they are not immune to problems. Identifying common radiator issues promptly is key to preventing major malfunctions that could potentially result in costly repairs or even engine damage.
Two prevalent complications often faced by vehicle owners are leaks and clogs within the radiator system. Leaks can stem from damaged hoses, a cracked radiator core, or even faulty gaskets. On the other hand, clogs may develop due to sediment buildup from inadequate coolant maintenance or external debris infiltrating the cooling system.
Troubleshooting these radiator issues entails systematic inspection and diagnosis. If a leak is suspected, visual examination for pooling coolant under the vehicle or a drop in coolant levels can help pinpoint the source.
Utilizing pressure tests for detecting leaks can aid in precise identification of compromised areas within the system. In cases of clogs, reduced coolant flow or overheating indicators signal potential blockages that necessitate flushing procedures or component replacement as necessary measures.

Regular maintenance plays a pivotal role in averting critical radiator failures. Simple practices like checking coolant levels routinely and ensuring proper fluid concentrations can significantly prolong the lifespan of your radiator.
Engaging in periodic inspections for signs of wear, corrosion, or degradation of key components permits timely interventions to address minor issues before they escalate into more severe complications. By adopting a proactive approach and adhering to prescribed maintenance schedules, individuals can safeguard their radiators against premature malfunction and extend their operational efficiency.
In essence, a well-maintained car engine radiator is vital for engine longevity and performance. Through diligent monitoring and preemptive action when anomalies arise, drivers can mitigate risks associated with common radiator malfunctions effectively.
By understanding how to identify issues like leaks and clogs early on and employing appropriate troubleshooting techniques promptly, individuals can uphold their radiators’ functionality while enhancing overall vehicle reliability and safety on the road.
Types of Car Engine Radiators.
Car engine radiators come in various types, each tailored to different vehicle needs and performance demands. Traditional radiators, often made of copper or aluminum, are the conventional choice found in many older vehicles.
These radiators boast excellent heat transfer properties and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they can be heavier compared to newer designs, impacting overall vehicle weight and efficiency.
In contrast, aluminum radiators have gained popularity due to their lightweight construction and superior heat dissipation capabilities. These radiators are commonly used in high-performance vehicles or racing cars where thermal management is crucial for optimal engine function.
While aluminum radiators offer improved cooling efficiency, they may be more susceptible to damage from road debris or corrosion compared to traditional models.
Electric radiators represent a modern innovation in cooling systems by utilizing electrical fans instead of relying on airflow through the radiator grille. This design allows for precise temperature control and faster response times during sudden temperature spikes.
Electric radiators are commonly found in hybrid or electric vehicles where reducing parasitic losses from engine-driven fans is essential for maximizing battery efficiency. Despite their advantages in energy efficiency, electric radiators may pose challenges related to power consumption and potential electronic failures.
Choosing the appropriate radiator type depends on factors such as vehicle usage patterns, climate conditions, and performance requirements. For example, a traditional radiator might suffice for daily commuting vehicles that prioritize reliability over maximum cooling capacity.
On the other hand, aluminum radiators could be ideal for off-road or high-speed driving scenarios that demand superior heat dissipation capabilities. Electric radiators shine in urban settings with frequent stop-and-go traffic patterns where precise thermal management plays a significant role in maintaining engine health and efficiency.
By understanding the nuances of each radiator type and evaluating them against specific vehicle needs, enthusiasts and mechanics can make informed decisions to optimize cooling system performance.
Efficiency and Cooling Capacity Factors.
In the realm of car engine radiators, several factors play pivotal roles in determining their efficiency and cooling capacity. One significant factor is the size of the radiator. Larger radiators have more surface area for heat dissipation, allowing for improved cooling performance.
Conversely, smaller radiators might struggle to dissipate heat effectively, especially in high-demand situations such as towing or extended periods of idling. Ensuring the radiator size matches the vehicle’s requirements is crucial for optimal functionality.
Another critical consideration is the material used in constructing the radiator. Traditional copper-brass radiators have been a longtime staple due to their excellent thermal conductivity properties.

However, aluminum radiators are gaining popularity due to their lightweight nature and superior heat transfer capabilities. The choice of material can significantly impact how efficiently the radiator transfers heat away from the engine, affecting overall performance.
Design also plays a vital role in determining a radiator’s efficiency. Factors like tube fin design, number of rows, and air flow patterns within the radiator core strongly influence its cooling capacity.
A well-designed radiator maximizes surface contact between coolant and ambient air, ensuring efficient heat exchange. Engineers leverage fluid dynamics and thermodynamics principles to optimize these design elements for enhanced cooling performance tailored to specific vehicle needs.
Thermal conductivity.
Furthermore, understanding thermal conductivity is key to grasping a radiator’s performance characteristics. Thermal conductivity measures how effectively a material transfers heat.
Materials with higher thermal conductivity values—such as aluminum—are better at swiftly moving heat away from the engine towards the coolant circulating through the radiator core. This property directly impacts how efficiently a radiator can cool an engine under varying operating conditions.
Ambient temperature also significantly affects the effectiveness of car engine radiators. Hot weather environments can hinder a radiator’s ability to dissipate heat adequately since there’s less temperature difference between the hot coolant and surrounding air.
In contrast, colder temperatures enhance heat transfer efficiency by promoting more substantial differentials that facilitate quicker cooling processes. Radiator designs must account for these environmental variables to ensure consistent performance across diverse climatic conditions.
By meticulously considering factors like size, material composition, design intricacies, thermal conductivity properties, and ambient temperature influences, engineers can fine-tune car engine radiators to achieve optimal cooling capacity essential for maintaining safe operating temperatures within vehicles across varied driving conditions and climates.
Maintaining Optimal Performance.
Ensuring optimal performance of car engine radiators is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of a vehicle’s cooling system. One key tip is to adhere to manufacturers’ guidelines for coolant flush intervals.
Regularly flushing the coolant removes contaminants, air bubbles, and sediment that can hinder heat transfer within the radiator. For example, in extreme conditions or heavy towing scenarios, more frequent coolant changes might be necessary to prevent overheating issues.
Monitoring coolant levels is another maintenance practice that shouldn’t be overlooked. Low coolant levels can lead to overheating and potential damage to the engine components.

Drivers should routinely check the coolant reservoir when the engine is cool to ensure it remains at the recommended level. Understanding that even minor leaks can significantly impact coolant levels underscores why vigilance in this area is paramount.
Recognizing signs indicating potential radiator problems can save both time and money by addressing issues early on. Signs like visible leaks under the vehicle, fluctuating temperature gauges, or unusual noises coming from the radiator area should prompt immediate investigation. Being proactive in addressing these signals can prevent catastrophic failures and unnecessary repair costs down the road.
In essence, maintaining optimal performance of car engine radiators lies in these simple yet impactful practices: adhere to recommended coolant flush intervals, monitor coolant levels regularly, and promptly address any warning signs of potential issues.
By incorporating these habits into routine vehicle maintenance schedules, automotive enthusiasts and mechanics alike can ensure that their car’s vital cooling system operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Future Innovations in Car Engine Radiators.
As technology continues to advance rapidly, the automotive industry is witnessing innovative developments in car engine radiators. One of the emerging technologies gaining traction is the concept of self-regulating cooling systems. These sophisticated systems are equipped with sensors that monitor the temperature of the engine and adjust coolant flow accordingly.
By automatically regulating the cooling process, these systems optimize efficiency and can help prevent overheating issues in vehicles. For instance, a self-regulating radiator could adapt to varying driving conditions, such as heavy traffic or high-speed highway cruising, ensuring optimal engine performance at all times.
Another exciting area of innovation revolves around smart temperature monitoring capabilities integrated into car engine radiators. Smart radiators utilize IoT (Internet of Things) technology to provide real-time data on coolant temperatures, fan speeds, and overall system health.
This information can be accessed remotely through a smartphone app or vehicle dashboard interface, enabling users to closely monitor radiator performance and receive alerts about potential malfunctions. For example, a driver could receive a notification if coolant levels are low or if there is a significant deviation from normal operating temperatures, allowing for prompt intervention before serious damage occurs.

The implications of these technological advancements extend beyond convenience for drivers; they also hold significant promise for sustainable practices within the automotive industry. By enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of car engine radiators, these innovations contribute to reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
Improved cooling system performance translates into enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, aligning with global efforts towards greener transportation solutions. As self-regulating cooling systems and smart temperature monitoring become more prevalent in vehicles, they have the potential to revolutionize not only how engines are cooled but also how we approach sustainability in automotive design and engineering.
Conclusion: Mastering Car Engine Radiator Basics.
In essence, an understanding of the intricate system that is a car engine radiator is crucial for automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineering students alike. As we have explored in this comprehensive guide, radiators play a critical role in vehicle cooling systems by facilitating heat exchange and maintaining optimal operating temperatures for internal combustion engines.
By delving into the components, common issues, types, efficiency factors, maintenance practices, and future innovations of car engine radiators, readers have acquired a solid foundation on these essential automotive components.
To master the basics of car engine radiators entails grasping the nuances of their design, function, and maintenance requirements. With knowledge on how coolant circulates to dissipate heat efficiently and prevent engine overheating problems like leaks or clogs, individuals can troubleshoot radiator issues effectively.
Furthermore, understanding the different types of radiators available and their respective advantages allows for informed decisions based on specific vehicle needs.
By focusing on efficiency factors like size and material selection while considering technological advancements such as self-regulating cooling systems or smart monitoring devices, one can appreciate the evolving landscape of radiator technology within the automotive industry.
In conclusion, mastering the intricacies of car engine radiators not only empowers individuals to address cooling system concerns competently but also opens doors to future innovations that promise enhanced performance and sustainability in vehicles.
Armed with this knowledge base, enthusiasts and professionals alike can navigate the realm of radiator technology with confidence and precision, ensuring efficient operation and longevity for their beloved machines.