7 Vital Components of Disc Braking Systems You Need to Know
Disc brakes are a crucial component of a car’s braking system, utilizing a combination of components to slow down or stop the vehicle. The main components of a disc brake system include:
Rotor or Brake Disc: This is the disc that rotates with the wheel and is made of steel, cast iron, or carbon-ceramic materials. It is designed to dissipate heat efficiently and is typically ventilated for better cooling.
Brake Pads: These are the components that press into the rotor to create friction and slow down the wheel. Brake pads are made of various materials such as organic, ceramic, and semi-metallic, each with its own characteristics and lifespan.
Piston: This is the hydraulic component that pushes the brake pads into the rotor. It is connected to the master cylinder and responds to the driver’s braking input.
Caliper: This is the housing that holds the brake pads and piston. It moves to clamp the brake pads onto the rotor, generating friction to slow down the vehicle.
Caliper Support: This is the structural component that supports the caliper and ensures proper alignment and movement.
Master Cylinder: This is the central component that generates hydraulic pressure to activate the brake system. It is connected to the brake pedal and distributes pressure to the brake calipers.
Reservoir Tank: This is the container that holds the brake fluid, which is essential for the hydraulic operation of the brake system.
Brake Pedals: These are the components that the driver presses to activate the brake system. They are connected to the master cylinder and transmit the driver’s input to the brake calipers.
Sensors: Some modern cars have sensors in the brake pads that monitor their condition and can alert the driver if they need to be replaced.
Hydraulic Hose: This is the hose that distributes brake fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers, ensuring proper hydraulic pressure.
How Disc Brakes Work.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, the following process occurs:
- The piston in the master cylinder forces hydraulic fluid into the brake lines.
- The hydraulic fluid pushes the piston in the brake caliper, which moves the brake pads into contact with the rotor.
- The friction generated by the brake pads slows down the wheel, and the vehicle comes to a stop.
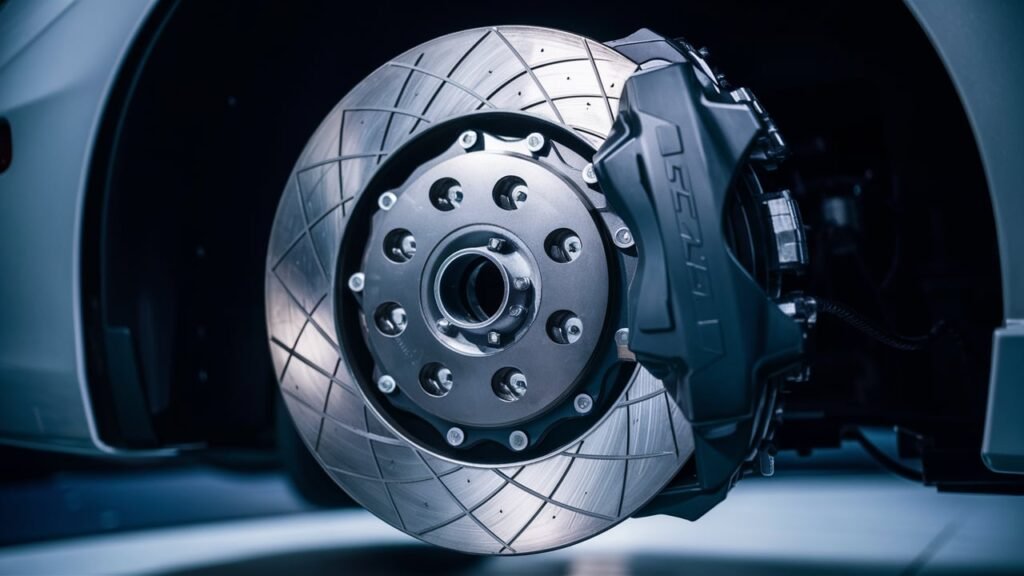

Maintenance and Replacement.
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the proper functioning of disc brakes. Key components that need to be checked and replaced include:
- Brake Pads: These should be replaced every 40,000 to 113,000 kilometers, depending on driving conditions and pad material
. Rotors: These can last up to 113,000 kilometers but may need to be resurfaced or replaced if damaged or worn out. Brake Fluid: This should be checked every 39,000 to 58,000 kilometers and replaced if necessary.
Understanding the components and functioning of disc brakes is essential for proper maintenance and ensuring safe driving.
When it comes to driving, safety is paramount. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind a vehicle’s disc braking system can make all the difference in crucial moments on the road.
Whether you are a car enthusiast fascinated by the engineering marvels under your hood or a DIY mechanic looking to elevate your knowledge, delving into the 7 vital components of disc braking systems is an essential journey. Get ready to explore the inner workings of brakes beyond mere brake pads and discs.
Among the unsung heroes of every stop and slow down, there lie crucial components like calipers, master cylinders, brake lines, and more waiting to be discovered. These elements intricately dance together to ensure your vehicle halts with precision when needed most.
So buckle up as we venture through the heart of a vehicle’s stopping power arsenal, understanding how each piece plays a vital role in keeping you safe on the road.
From materials used for brake lines to different types of calipers, get ready to unlock insights that will not only deepen your appreciation for car mechanics but also empower you with valuable knowledge for enhanced driving performance. Let’s unravel the mysteries beneath those sleek wheels and dive headfirst into the world of disc braking systems!
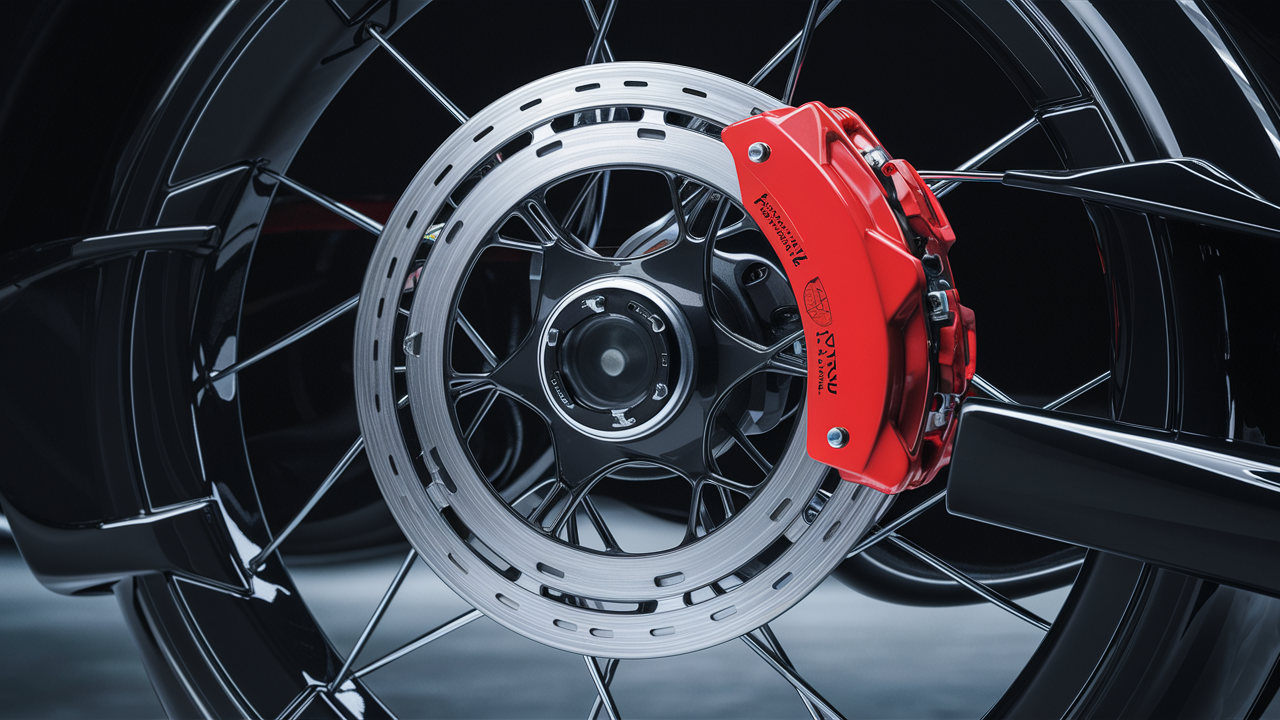
Brake Discs.
When it comes to the essential components of a disc braking system, brake discs play a pivotal role in ensuring safe and reliable braking performance. The brake discs, also known as rotors, are responsible for generating the friction needed to slow down or stop the vehicle when the brakes are applied.
As the brake pads clamp down on the spinning discs, the resulting friction generates heat and kinetic energy conversion, enabling your car to decelerate smoothly.
There are various types of brake discs available in the market, each designed with unique features to cater to different driving needs. Vented brake discs have channels between two braking surfaces that aid in heat dissipation, ideal for high-performance vehicles that undergo intense braking.

Drilled brake discs have holes drilled through them to reduce heat buildup and improve wet weather performance, favored by sports car enthusiasts. Slotted brake discs feature slots cut into the surface that help maintain consistent contact between the pad and rotor for enhanced braking stability.
Choosing high-quality brake discs is vital for optimal braking performance and safety. Lower-quality discs may lead to issues like excessive wear, reduced stopping power, or even brake failure under extreme conditions.
Investing in reputable brands or performance-oriented brake disc models can ensure longevity and reliability while offering better heat dissipation characteristics for sustained performance during demanding driving situations.
Remember, when it comes to your safety on the road, opting for top-notch brake discs is a decision that can make a significant difference in your overall driving experience.
Calipers.
Calipers are vital components in a disc braking system that play a crucial role in bringing your vehicle to a halt safely. These devices are responsible for applying the necessary pressure to the brake pads, which then make contact with the rotating brake discs to slow down or stop the wheels.
Understanding the different types of calipers can provide insights into their unique features and how they influence braking performance. There are three main types of calipers: floating, fixed, and sliding. Floating calipers are commonly found in most vehicles and have pistons only on one side that press against the inner brake pad.
Fixed calipers, on the other hand, have pistons on both sides and provide more even pressure distribution over the brake pads, resulting in improved braking efficiency. Sliding calipers work by moving laterally to apply pressure to both sides of the rotor simultaneously, offering consistent braking performance across all driving conditions.

To ensure optimal braking performance and safety on the road, it is essential to maintain and service your calipers regularly. Over time, calipers can accumulate dirt, debris, or corrosion that may affect their functionality.
Regular inspection of caliper components such as pistons, seals, and slide pins can help identify potential issues early on and prevent brake problems down the line. By keeping your calipers well-maintained, you can maximize their lifespan and contribute to smooth braking experiences every time you hit the road.
Brake Pads.
Brake pads play a critical role in the disc braking system as they are responsible for creating friction against the brake disc to slow down or stop the vehicle effectively. Think of them as the essential interface between your foot pressing on the brake pedal and the car coming to a halt.
When you push on the brakes, these pads clamp down on the spinning brake discs, converting kinetic energy into heat through friction, ultimately bringing your vehicle to a controlled stop.
There are various types of brake pad materials available, each offering distinct advantages based on driving needs. For example, ceramic brake pads are known for their quieter operation and cleaner wheels due to less dust generation.
On the other hand, organic brake pads are more budget-friendly and produce minimal noise while offering good initial bite. Additionally, semi-metallic brake pads are popular for their durability and resistance to fade under high-temperature conditions, making them suitable for performance driving enthusiasts seeking consistent stopping power.
Recognizing signs that indicate the need for replacing brake pads is crucial for road safety. Squealing or grinding noises when applying brakes can be indicators of worn-out pads causing metal-to-metal contact with the discs.
Vibrations or a mushy pedal feel can also suggest deteriorating brake pads. Regularly inspecting and proactively replacing brake pads when necessary not only ensures optimal braking performance but also prevents potential damage to other components of the braking system, contributing to safer driving experiences on the road.
The Roke of Brake fluid.
Brake fluid plays a crucial role in the operation of a vehicle’s braking system, acting as the medium that transfers the force applied to the brake pedal to the actual brakes themselves. It is essential for creating hydraulic pressure within the system, allowing for effective braking performance.
Different types of brake fluids are available, with common ones being DOT 3, DOT 4, and DOT 5. These variations differ in their compositions and boiling points, catering to various vehicles’ specific requirements.
For instance, a high-performance sports car might benefit from a higher boiling point fluid like DOT 4 to withstand intense braking conditions compared to a daily commuter vehicle that can work efficiently with a standard DOT 3 fluid.
Maintaining proper levels of brake fluid is paramount for ensuring consistent and reliable braking efficiency. Regular inspection of the brake fluid reservoir and checking for any discoloration or contaminants is essential in monitoring its condition.

Additionally, following manufacturer guidelines on when to replace the brake fluid is crucial in preventing brake system malfunctions due to degraded or contaminated fluid. As an example, neglecting to change old brake fluid in time could lead to decreased braking responsiveness or even complete failure when driving at high speeds, compromising safety on the road.
An interesting tip for drivers seeking optimal braking performance is considering upgrading to a high-quality synthetic brake fluid that offers enhanced heat resistance and longevity compared to conventional options.
This upgrade can be particularly beneficial for vehicles used in extreme driving conditions or heavy-duty applications where consistent braking power is vital. By taking proactive measures such as choosing the right type of brake fluid and adhering to maintenance schedules, drivers can maximize their braking system’s longevity and ensure safe and smooth stops every time they hit the brakes.
Master Cylinder: The Hydraulic Heart of Your Braking System.
The master cylinder plays a pivotal role in the functionality of your vehicle’s braking system by converting the mechanical force generated when you press on the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure.
This hydraulic pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines to the calipers, where it engages the brake pads against the rotor, ultimately slowing down or stopping your car. Without a properly functioning master cylinder, your brakes would lose their effectiveness, potentially leading to dangerous situations on the road.
One telltale sign of a failing master cylinder is a spongy or sinking brake pedal. If you notice that your brake pedal feels different than usual or goes all the way to the floor before engaging the brakes, it could indicate a problem with the master cylinder.

Additionally, if you experience any loss of braking power or notice leaks around the master cylinder reservoir, these are red flags that warrant immediate attention. Ignoring these warning signs can compromise your ability to stop safely and put you at risk while driving.
Routine inspections and maintenance of your vehicle’s master cylinder are paramount to ensure optimal braking performance. Regularly checking for leaks, monitoring fluid levels, and ensuring proper sealing of components can help prevent potential issues with the master cylinder.
By addressing any abnormalities promptly and adhering to recommended maintenance schedules, you can extend the lifespan of your master cylinder and maintain reliable braking performance when you need it most. Remember, taking care of this unsung hero of your braking system can make a world of difference in your driving safety and peace of mind.
The Role of Brake lines.
Brake lines play a critical role in the hydraulic system of your vehicle’s braking mechanism. Serving as the conduits that carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the individual brakes at each wheel, these lines must be durable and free from any defects to ensure reliable brake performance.
Commonly, brake lines are crafted from materials like steel, stainless steel, or rubber. Steel lines offer high durability and can withstand significant pressure, making them ideal for heavy-duty braking systems. On the other hand, stainless steel lines provide excellent corrosion resistance, extending their lifespan and reliability in various driving conditions.
Regular inspection of brake lines is paramount in maintaining optimal brake function and safety on the road. Examine these crucial components for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks which could compromise their integrity and lead to brake failure.

For instance, if you spot rust or fraying on a steel brake line during maintenance checks, it’s essential to address this immediately to prevent potential issues when applying the brakes. By proactively monitoring the condition of your brake lines, you can identify problems early on and take necessary corrective actions before they escalate into more significant safety concerns.
Imagine cruising down a winding mountain road only to find your brakes feel spongy or unresponsive due to a leaking brake line – emphasizing why regular checks are vital. Different materials used in manufacturing these channels have specific characteristics that impact their longevity and performance under pressure; grasping these nuances can guide maintenance decisions.
Therefore, understanding how varied material choices influence the durability and reliability of brake lines can empower car enthusiasts and DIY mechanics to make informed choices when selecting replacement parts or conducting inspections themselves.
Remember, ensuring your brake lines are well-maintained is not just about preserving your vehicle but also about safeguarding yourself and others sharing the road with you.
Understanding the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
In conclusion, mastering the knowledge of the essential components of disc braking systems is crucial for every car enthusiast, DIY mechanic, driver, or automotive student. Among these vital components, the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) stands out as a technology that significantly enhances safety on the road.
By preventing wheels from locking up during abrupt stops, ABS ensures better steering control and shorter stopping distances, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents and collisions.
It is paramount for individuals to comprehend how ABS operates and to acknowledge its maintenance requirements for optimal functionality. Embracing this understanding not only improves driving confidence but also contributes to a safer driving experience for both drivers and passengers alike.
So, remember, when it comes to disc braking systems, knowing the importance of ABS can be a lifesaver in critical moments on the road.