Unraveling the Complexity of Anti-lock Braking Systems
Here is a concise summary of the complexity of anti-lock braking systems (ABS):ABS is a sophisticated safety system that uses advanced electronics and sensors to prevent wheel lock-up during braking. The key components of an ABS include :
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The central computer that monitors wheel speeds and controls the braking system.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Sensors at each wheel that detect the rotational speed of the wheels.
- Hydraulic Valves: Valves that can rapidly modulate the brake pressure to each wheel independently.
- Hydraulic Pump: A pump that can increase brake pressure when needed.
The ECU constantly monitors the wheel speeds using the sensors. When it detects a wheel is about to lock up, it automatically reduces the brake pressure to that wheel through the valves . This prevents the wheel from locking up and allows the driver to maintain steering control.
The ECU can adjust the brake pressure up to 15 times per second, much faster than a human driver could manually pump the brakes . This complex, real-time control is what makes ABS an effective safety system.
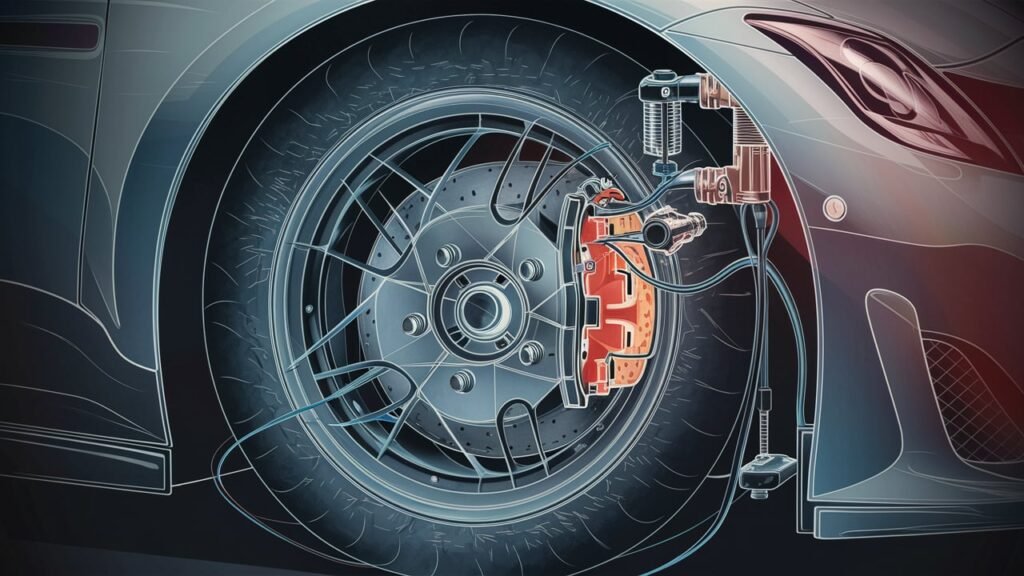
The intricate arrangement of sensors, valves, pumps, and the electronic control unit increases the overall complexity of ABS compared to traditional braking systems . This complexity also makes ABS more expensive to maintain and repair compared to non-ABS brakes .
In summary, the use of advanced electronics, sensors, and hydraulic components to provide automatic, independent control of each wheel’s braking force is what makes ABS a sophisticated and complex safety system in modern vehicles.
In the realm of automotive engineering, Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) stand as a pivotal innovation that has redefined vehicle safety standards. ABS technology serves as an indispensable element within modern vehicles, revolutionizing braking dynamics to ensure enhanced stability and control in diverse driving conditions.
As we delve deeper into the intricate world of ABS, a profound understanding of its complexities becomes imperative for auto enthusiasts, mechanics, engineers, and automotive students alike.
The significance of ABS transcends mere functionality; it embodies a paradigm shift towards proactive safety measures on the roads. By mitigating the risks associated with wheel lock-up during braking maneuvers, ABS fundamentally alters the trajectory of vehicular safety.
From augmenting steering responsiveness to preventing dangerous skids on slippery surfaces, the intricate interplay of components within an ABS system manifests a seamless fusion of technological prowess and real-time hazard management.
As we navigate through the intricacies of ABS technology in this comprehensive discourse, prepare to unravel the multifaceted layers that underscore its critical role in modern automotive design.
Understanding the Basics of ABS.
Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) represent a crucial advancement in automotive safety technology. ABS is a sophisticated system designed to prevent wheel lock-up when sudden, hard braking occurs, especially during emergency situations.
This preventative measure is vital as brake lock-up can lead to loss of steering control, causing skidding and compromising overall vehicle stability. By pulsating the brakes multiple times per second, ABS ensures that the wheels maintain traction with the road surface, ultimately allowing the driver to steer the vehicle even under intense braking pressure.
The core functionality of ABS relies on sensors strategically placed throughout the vehicle to monitor individual wheel speeds continuously. These sensors provide real-time data to the electronic control unit (ECU), essentially acting as the brain of the system.
The ECU processes this information rapidly and modulates hydraulic pressure to each wheel’s brake independently through solenoid valves. Consequently, ABS allows for variable braking force distribution among all four wheels, effectively preventing any one wheel from locking up while maintaining optimal stopping power.

Notable components within an ABS system include speed sensors, hydraulic modulators, and pump motors working harmoniously to deliver reliable anti-lock capabilities.
To illustrate how ABS operates efficiently in practice: Imagine a scenario where a driver encounters a sudden obstacle on wet asphalt necessitating aggressive braking. Without ABS, excessive brake pressure could cause the wheels to lock up on the slick surface, leading to loss of control and potential collision.
In contrast, with an active ABS system in place, sensors detect individual wheel speeds slowing down too quickly compared to others and promptly engage rapid brake modulation to prevent lock-up. As a result, drivers can maneuver around obstacles more effectively due to enhanced stability and reduced stopping distances provided by this intricate anti-lock technology.
Evolution of ABS Technology.
The evolution of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) traces back to the mid-20th century when the concept was first explored by automotive engineers as a solution to prevent skidding and improve vehicle control during braking.
In 1958, the American automotive company Chrysler introduced one of the earliest forms of an ABS system known as “Sure Brake.” This system utilized speed sensors on each wheel to detect wheel lock-up and then released brake pressure accordingly, paving the way for future advancements in ABS technology.
Over the years, ABS systems have undergone substantial advancements, transitioning from rudimentary mechanical systems to highly sophisticated electronic control units (ECUs).
Modern ABS systems now incorporate multiple sensors such as wheel speed sensors, accelerometers, and hydraulic modulators that work in harmony to regulate brake pressure and prevent wheel lock-up more effectively.
Additionally, advancements in microprocessor technology have significantly enhanced the processing capability of ABS systems, allowing for quicker response times and improved performance under varying road conditions.

Technological innovations have revolutionized the performance and efficiency of ABS by introducing features such as Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control System (TCS) as integrated components of ABS units. ESC enhances vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction during cornering or sudden maneuvers, while TCS limits wheel spin during acceleration on slippery surfaces.
These advancements not only improve overall vehicle safety but also contribute to smoother handling and enhanced driver confidence behind the wheel. The continuous integration of advanced technologies into ABS systems highlights a relentless pursuit within the automotive industry to enhance safety standards and optimize braking performance for modern vehicles.
Benefits of ABS.
Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) offer a myriad of benefits crucial for ensuring vehicle safety and stability. One primary advantage is the improved vehicle control during emergency braking situations.
ABS systems work by monitoring wheel speed and automatically adjusting brake pressure to prevent wheel lock-up. This dynamic control allows drivers to maintain steering control even under hard braking, reducing the risk of accidents caused by skidding.
Moreover, ABS plays a vital role in preventing skidding and loss of traction on slippery surfaces. In instances where traditional braking systems could lead to loss of control due to wheels locking up on icy or wet roads, ABS intervenes proactively. By modulating brake pressure rapidly through its sensors and hydraulic valves, ABS enables vehicles to stop more effectively without sacrificing stability.
Enhanced steering ability while braking, particularly in hazardous conditions, is another key benefit offered by Anti-lock Braking Systems. When faced with sudden obstacles or sharp turns that require swift deceleration, ABS ensures that the driver can maintain directional control without veering off course.
This feature is especially valuable in scenarios where split-second decisions are necessary to avoid collisions or navigate safely through challenging road conditions.
Challenges and Limitations of ABS.
Despite the numerous benefits Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) offer, they are not without their challenges and limitations, which can influence their effectiveness in certain conditions. Factors like road conditions and tire quality play a significant role in how well ABS functions.
For instance, on uneven or gravel roads, ABS may struggle to provide optimal braking control due to varying surface conditions. Similarly, worn-out or low-quality tires can hinder the system’s ability to prevent wheel lock-up efficiently.
Older or malfunctioning ABS systems present common issues that can compromise overall braking performance. For example, sensor malfunctions can lead to erratic behavior in the ABS system, causing inconsistent brake pressure application and potentially affecting vehicle stability during braking.
Moreover, deteriorating hydraulic components within the ABS unit can result in delayed or inadequate brake engagement, posing safety risks for the driver and passengers.

To overcome these limitations and maximize the benefits of ABS, various strategies can be implemented. Regular maintenance checks and timely replacement of worn components can help ensure the smooth operation of the system.
Additionally, staying informed about software updates or recalls related to ABS can address potential issues before they escalate. In cases where road conditions are challenging, such as icy surfaces, adapting driving techniques by increasing following distances and maintaining moderate speeds can aid in optimizing ABS functionality.
By understanding these challenges and proactively addressing them through proper maintenance and informed driving practices, drivers can enhance the effectiveness of their vehicle’s anti-lock braking system. Adopting a proactive approach to overcoming limitations ensures that ABS continues to serve its vital role in enhancing vehicle safety and stability on diverse road surfaces.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for ABS.
Ensuring the optimal functionality of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) requires regular maintenance practices. One essential maintenance task is inspecting the ABS sensors for any dirt, debris, or damage that could affect their performance.
Cleaning the sensors and ensuring they are properly positioned can help maintain accurate wheel speed readings, crucial for ABS operation. Additionally, checking and replacing worn brake pads and rotors is vital to prevent premature wear on ABS components due to increased braking force requirements.
Warning signs of potential issues with an ABS system should not be ignored. One common indicator of a malfunctioning ABS system is the illumination of the ABS warning light on the dashboard. This warning light signals a fault in the system and prompts immediate attention to diagnose and address the underlying problem.
Other symptoms like unusual noises during braking, pulsation in the brake pedal, or longer stopping distances than usual can also signal potential ABS issues that warrant inspection by a trained professional.

Diagnosing and addressing common problems with ABS components involves systematic troubleshooting steps. When faced with erratic ABS behavior, such as unanticipated brake pulsations or unexpected activation of the system under normal braking conditions, conducting a diagnostic scan using specialized OBD-II scanners can help pinpoint specific faults within the system.
From there, technicians can focus on testing individual components like solenoids, modulators, or control units to identify defective parts that require repair or replacement for restoring proper ABS functionality. By following structured troubleshooting procedures, mechanics can efficiently address ABS issues and ensure continued safety on the road for drivers relying on this critical braking technology.
Training and Education in ABS Technology.
Proper training is crucial for mechanics and engineers engaging with Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) to ensure the accurate diagnosis and resolution of issues. Institutions offering specialized courses on ABS technology equip individuals with theoretical knowledge and practical skills essential for working on these sophisticated systems.
These programs cover a wide array of topics, from the fundamental principles of ABS operation to advanced troubleshooting techniques. For example, automotive technicians learn about sensor calibration, hydraulic pressure modulation, and electronic control unit diagnostics, enabling them to address intricate ABS malfunctions effectively.
Educational programs focused on ABS not only delve into the technical aspects but also emphasize the significance of safety protocols and ethical considerations when dealing with braking systems.
Hands-on training sessions allow participants to simulate scenarios where ABS intervention is critical, fostering a comprehensive understanding of how these systems operate in real-world situations.
Institutions often collaborate with leading automotive manufacturers to provide access to cutting-edge technologies and insights into the latest advancements in ABS engineering. This exposure ensures that aspiring professionals stay abreast of industry developments and are well-prepared to handle evolving ABS technologies.
Automotive students keen on specializing in ABS engineering can explore a range of resources tailored to enhance their knowledge and skills in this field. Online forums, webinars by industry experts, and supplementary reading materials offer valuable insights into the intricate workings of modern ABS systems.
Additionally, workshops conducted by renowned automotive institutions provide hands-on experience with state-of-the-art equipment used in diagnosing and repairing ABS components. These resources serve as invaluable tools for students aspiring to carve a niche in ABS engineering, offering them avenues for continuous learning and professional growth in this specialized domain.
Future Trends in Anti-lock Braking Systems.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) points towards exciting advancements that promise to revolutionize vehicle safety. One key area of future development lies in the seamless integration of ABS technology with autonomous driving systems.
The marriage of ABS with self-driving capabilities offers a synergy that can drastically reduce accidents and enhance overall road safety standards. Imagine vehicles equipped not only to prevent wheel lock-up during braking but also capable of communicating with surrounding vehicles and infrastructure to preemptively adjust braking patterns for optimal control and accident avoidance.
Furthermore, future generations of ABS are expected to delve deeper into predictive analysis and machine learning algorithms. These technological enhancements will empower ABS systems to adapt dynamically to changing road conditions, driver behavior patterns, and even vehicle-specific characteristics.
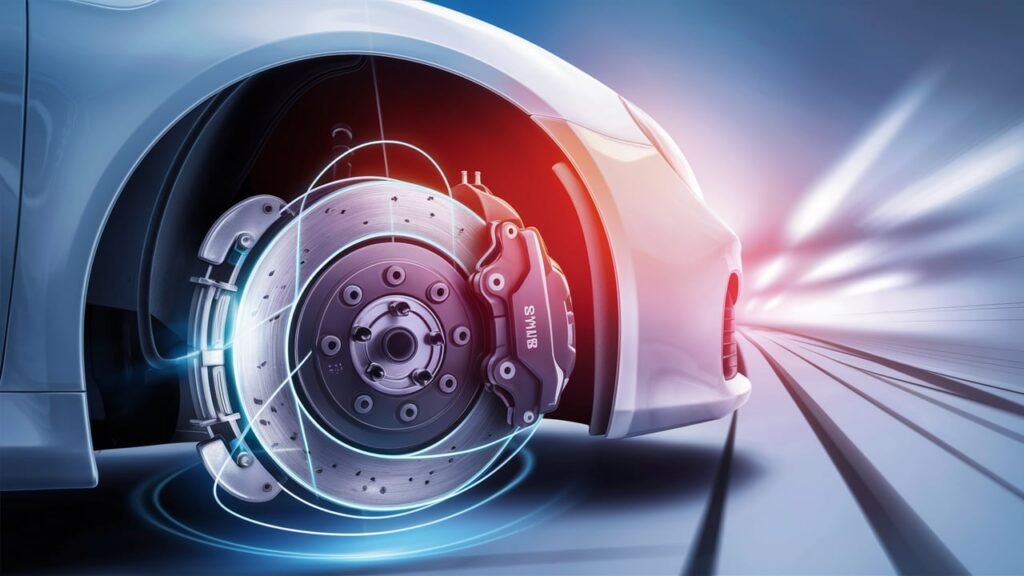

By utilizing real-time data inputs from sensors, cameras, and vehicle-to-vehicle communication networks, next-gen ABS solutions aim to provide customized braking responses tailored precisely to each driving scenario. This predictive capability is set to elevate both the performance and safety margins of ABS-equipped vehicles significantly.
In addition to improving collision prevention mechanisms, the evolution of ABS is likely to embrace energy efficiency as a core focus area. With sustainability gaining momentum in the automotive industry, future ABS iterations are anticipated to optimize braking algorithms for minimal energy wastage.
Strategies such as regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy into usable electrical power during deceleration, could become standard features in advanced ABS systems.
By combining safety with eco-conscious design principles, these cutting-edge solutions are poised not only to save lives but also contribute positively towards reducing carbon footprints associated with conventional braking systems.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in automotive technology, where interconnected smart vehicles are reshaping transportation paradigms worldwide, Anti-lock Braking Systems emerge as pivotal players in ensuring safer road environments for all stakeholders.
The convergence of advanced technologies like autonomous driving capabilities, predictive analytics, and energy-efficient designs within ABS frameworks heralds a promising landscape where accidents are minimized, sustainability is prioritized, and road safety standards are elevated far beyond what we ever deemed possible.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of Anti-lock Braking Systems.
In conclusion, Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) stand as fundamental components within modern vehicles’ safety frameworks. ABS technology has significantly contributed to enhancing vehicle stability and control during emergency braking scenarios, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents on roads worldwide.
The relentless evolution in braking technologies, exemplified by ABS advancements, underscores the automotive industry’s commitment to continuously improving safety measures for drivers and passengers alike.
As we look ahead, the trajectory of ABS points towards an integration with autonomous driving systems and a seamless synergy with future innovations in vehicle safety. This progression highlights a concerted effort towards not only reducing accidents but also setting higher standards for road safety globally.
Embracing these advancements underscores the importance of ABS in paving the way for safer journeys, reinforcing its pivotal role in ensuring secure transportation experiences for all road users.